Ceramic Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
The thermal expansion of materials is usually expressed in terms of linear expansion coefficient or bulk expansion coefficient. Thermal expansion coefficient is one of the main physical properties of materials, and it is an important index to measure the thermal stability of materials. Under constant pressure, the change in length, area or volume caused by a change in unit temperature is called the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE).
What is the coefficient of thermal expansion of ceramics?
The coefficient of thermal expansion of ceramics refers to the proportion of the length of the material changing with temperature at unit temperature. It is usually expressed as α in units per ° C. The coefficient of thermal expansion of different kinds of ceramics may be different, in general, the coefficient of thermal expansion of ceramics is between 3×10^-6/℃ ~ 10×10^-6/℃.
Effect of thermal expansion coefficient on ceramic application
The coefficient of thermal expansion of ceramics is generally much smaller than that of metals. This means that when ceramics and metals are joined together, temperature changes can cause stress between them. If these stresses exceed the strength of the material, cracks or damage can result.
In the production and application of ceramic products, the influence of thermal expansion coefficient should be reduced as much as possible. For example, when making important parts, designers need to consider the coefficient of thermal expansion to ensure that the product will not be damaged due to temperature changes during use.
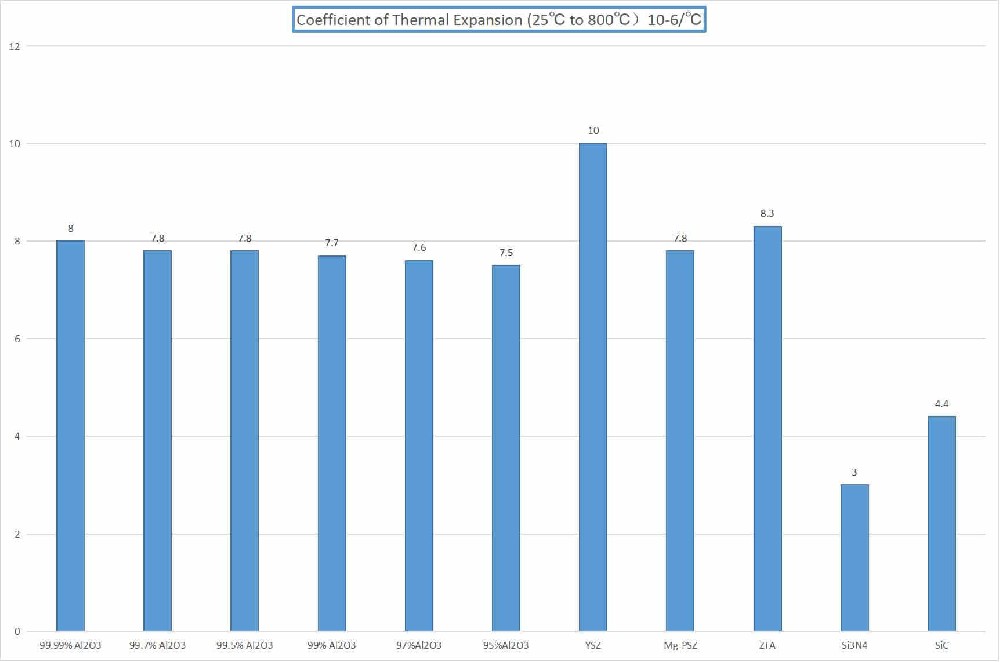
Thermal expansion coefficient of common ceramic materials
The thermal expansion coefficient of different kinds of ceramic materials is also different. The following is the range of thermal expansion coefficient of some common ceramic materials:
1. Alumina ceramics: α=7×10^-6/℃ ~ 9×10^-6/℃
2. Silicon nitride ceramics: α=3.2×10^-6/℃ ~ 4.5×10^-6/℃
3. Boron carbide ceramics: α=4.5×10^-6/℃ ~ 6.5×10^-6/℃
Method of reducing coefficient of thermal expansion
In order to reduce the negative impact of the thermal expansion coefficient of ceramics on practical applications, the following methods can be used:
1. Select ceramic materials with small thermal expansion coefficient for production;
2. Add an appropriate amount of glass phase during production to adjust its thermal expansion coefficient;
3. Use reasonable structural design and matching size in the design to reduce the influence of thermal stress.