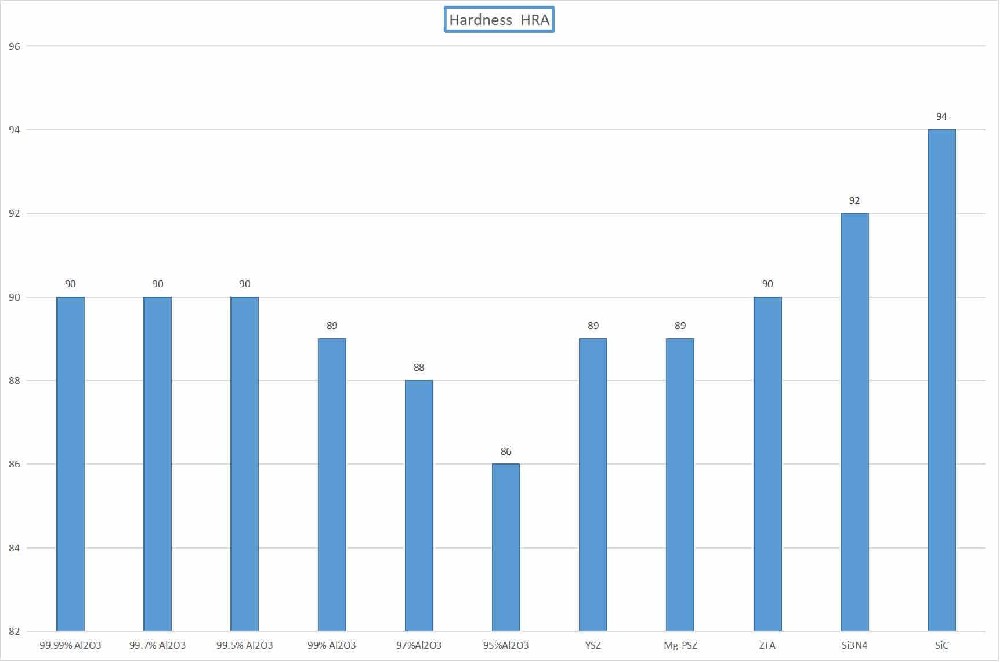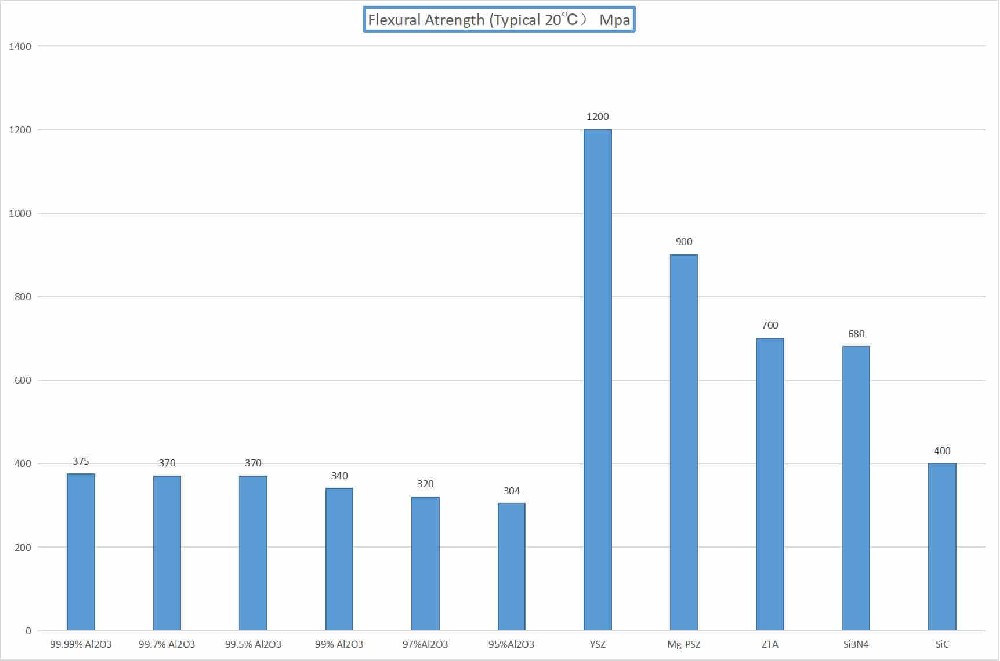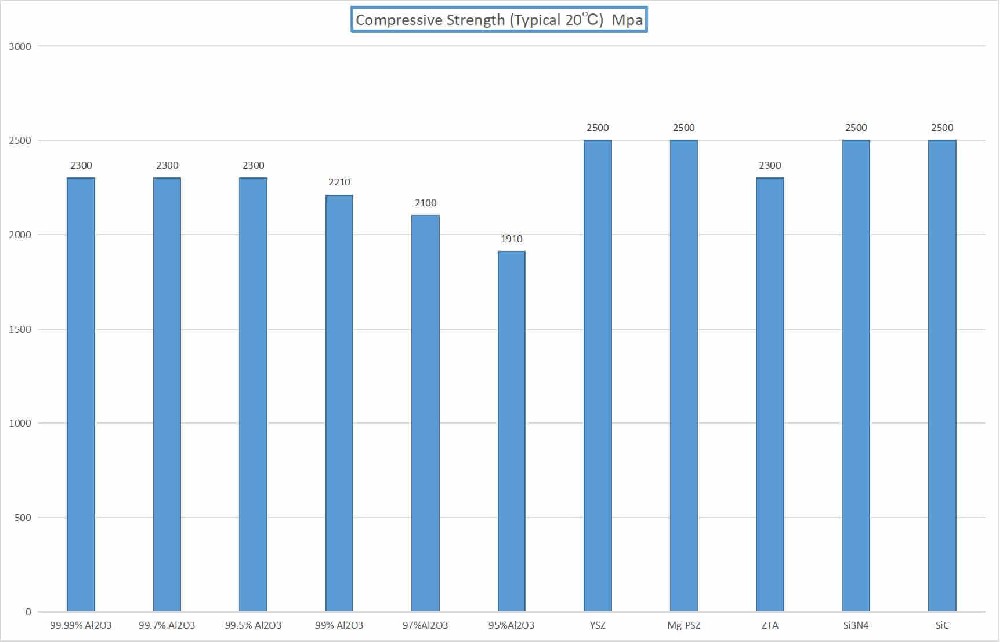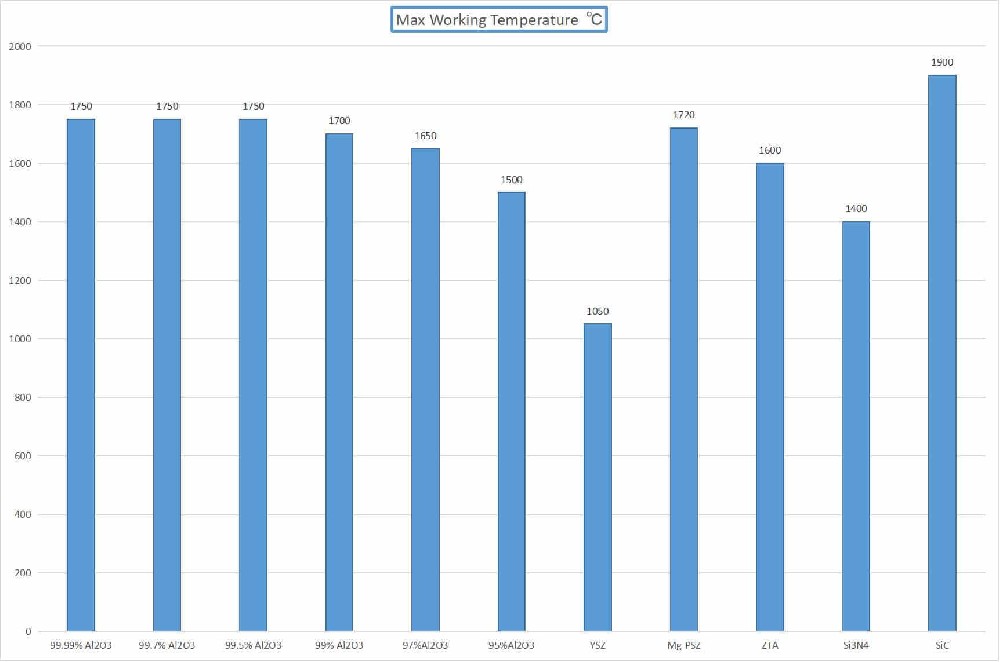
Ceramic Density
Ceramic density refers to the mass per unit volume, usually expressed in g/cm³.
Ceramic is a kind of non-metallic material, the density of ceramic is mainly affected by the type of material, structure and production process. In general, ceramics have a higher density because their material density is relatively large. The density of ceramics directly affects the hardness, robustness and texture of ceramics.
Industrial ceramics is a kind of ceramic material used in industrial products, such as ceramic tools, ceramic bearings, ceramic seals, etc., and its density is usually between 3.0-3.5g/cm³. The high density of industrial ceramics indicates its strong wear resistance and corrosion resistance. Industrial ceramics are mainly made of alumina, aluminum borate and other materials, and are fired at high temperatures. Industrial ceramics have the characteristics of high hardness, high temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, etc., and are widely used in automotive, aerospace, chemical and other fields.
What is the density of the ceramic
The density of ceramics is generally between 2.2 and 3.8g/cm³, and there are certain differences in the density of different types of ceramics, which can be calculated and compared according to the composition and structure of the material.
The meaning and calculation method of density
Density is the mass of an object per unit volume, usually expressed in g/cm³. The formula is: density = mass ÷ volume. Before understanding the density of ceramics, let's briefly introduce the calculation method of density.
The density range and difference of ceramics
A ceramic is a non-metallic, inorganic, amorphous or partially crystalline material with a density generally between 2.2 and 3.8g/cm³. In this range, there are also certain differences in the density of different types and uses of ceramics. Here are some specific examples:
Alumina ceramics
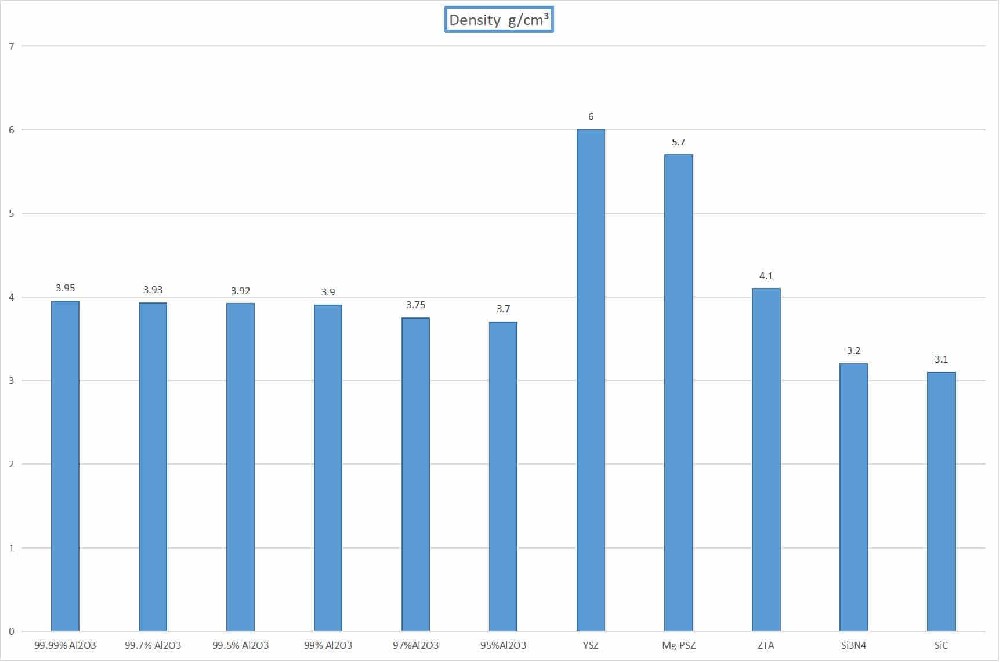
The density of alumina ceramics is about 3.5g/cm³, which is a kind of advanced ceramic material with high hardness and strong corrosion resistance.
Zirconia ceramics
The density of zirconia ceramics is about 5.6g/cm³, which has high wear resistance and thermal stability, and is often used in the manufacture of high-end wear-resistant parts.
The reason for the difference in the density of different ceramics
The density difference of different ceramics is mainly due to the difference in their material composition and structure. The density of some ceramics is lower because the material contains many pores, resulting in a relatively light mass. Other ceramics have a higher density because of their high crystallinity and uniform composition.
The density of ceramics varies depending on their type and manufacturing process, generally ranging from 2.0 to 4.5 g/cm ³. For example, the density of alumina ceramics is about 3.5 to 4.0 g/cm ³, while the density of silicon nitride ceramics may be as high as 3.2 to 3.4 g/cm ³. These values are based on standard test methods and professional data sources in the field of materials science.
Ceramic density Overview
Ceramic is a kind of inorganic non-metallic material, which has a wide range of uses and excellent properties. Density, as an important physical property of ceramic materials, has an important impact on its performance and application. The density of a ceramic is the mass of the ceramic material per unit volume, usually expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). Different types of ceramics and different manufacturing processes can lead to significant differences in ceramic density.
Influencing factors of ceramic density
1. Material composition: The composition of the ceramic has a direct impact on its density. For example, alumina ceramics have a relatively high density due to the high density of alumina components. The density of silicon nitride ceramics is also at a high level due to the special structure of silicon nitride molecules.
2. Manufacturing process: The manufacturing process of ceramics will also affect its density. In the process of ceramic preparation, factors such as temperature, pressure and time will affect the microstructure and density of the ceramic. For example, high temperature sintering can make ceramic particles more closely bonded together, thus increasing the density of the ceramic.