Ceramic Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength of ceramics and its application
The dielectric strength of a ceramic refers to the maximum electric field strength that a unit thickness ceramic can withstand under the action of an electric field, usually 100-500 V/mil
What is the dielectric strength of ceramics
The dielectric strength of ceramic refers to the maximum electric field strength that ceramic can withstand per unit thickness under the action of electric field. It is usually described in terms of voltage, potential difference, electric field strength and electric flux density.
In the microstructure of ceramics, electrons and ions move in the lattice, and when the electric field is strengthened, the movement of these electrons and ions becomes more intense, making the ceramic conductive or destructive. Therefore, the dielectric strength of a ceramic can also be used to evaluate its electrical properties.
Dielectric loss is a physical quantity that describes the energy loss of an electric field when it passes through a medium. The smaller the dielectric loss, the higher the transmission efficiency of the medium to the electric field. The dielectric loss of ceramic materials is usually less than 0.001.
The dielectric strength of ceramics is affected by many factors, including sintering temperature, preparation process, ceramic composition, crystal structure and so on. Generally, the dielectric strength of ceramics is around 100-500 V/mil.
Overview of the dielectric strengthof ceramics
Dielectric strength is a measure of the ability of a substance to respond to an electric field, and it represents the ability of a dielectric to store electrical energy. Ceramic is a kind of non-metallic material with oxide as the main component, which has the advantages of good insulation performance, high strength and hardness. Therefore, ceramics have a wide range of applications in electronic, photoelectric, magnetic and other fields.
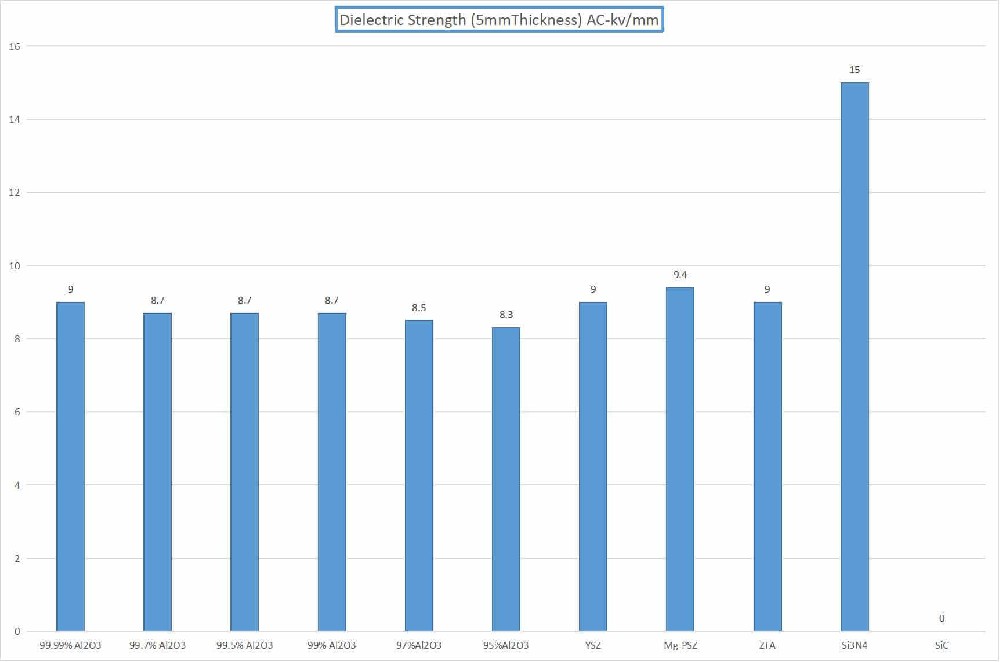
The dielectric strength of ceramics varies depending on the composition, crystal structure, temperature and other factors, usually around 1-10. Among them, the dielectric strength of alumina (Al2O3) is 9-10, the dielectric strength of zirconia (ZrO2) is about 20, and the dielectric strength of iron oxide (Fe2O3) is smaller, only about 4.
Dielectric coefficients of different dielectric ceramics
1. Aluminum oxide ceramics
Aluminum oxide ceramics is one of the materials with the highest intermediate electric strength of dielectric ceramics. Its dielectric strength is between 9-10, and the dielectric loss Angle tangent is below 1×10-4.
2. Magnesium oxide ceramics
Magnesium oxide ceramics is a material with the second highest dielectric strength, the dielectric strength is about 7-8, and the dielectric loss Angle tangent is also very small, usually less than 5×10-4.
3. Zirconium based ceramics
The dielectric strength of zirconium based ceramics is about 26, and the dielectric loss Angle tangent is less than 1×10-3. Its high dielectric strength and low dielectric loss Angle tangent make it suitable for high-precision electronic devices, such as filters, antennas, etc.
4. Strontium titanate ceramics
The dielectric strength of strontium titanate ceramics is between 300 and 1000, and the dielectric loss Angle tangent is less than 0.3. Its dielectric properties are better than most existing ceramic materials, making it an ideal microwave ceramic material.