Introduction to machining methods of precision ceramics
Ceramic machining technology is a complex and fine process, including machining, heat treatment, polishing, coating, surface softening, etc., all these technologies are essential, only the mastery of these technologies, in order to produce high-quality ceramic products.
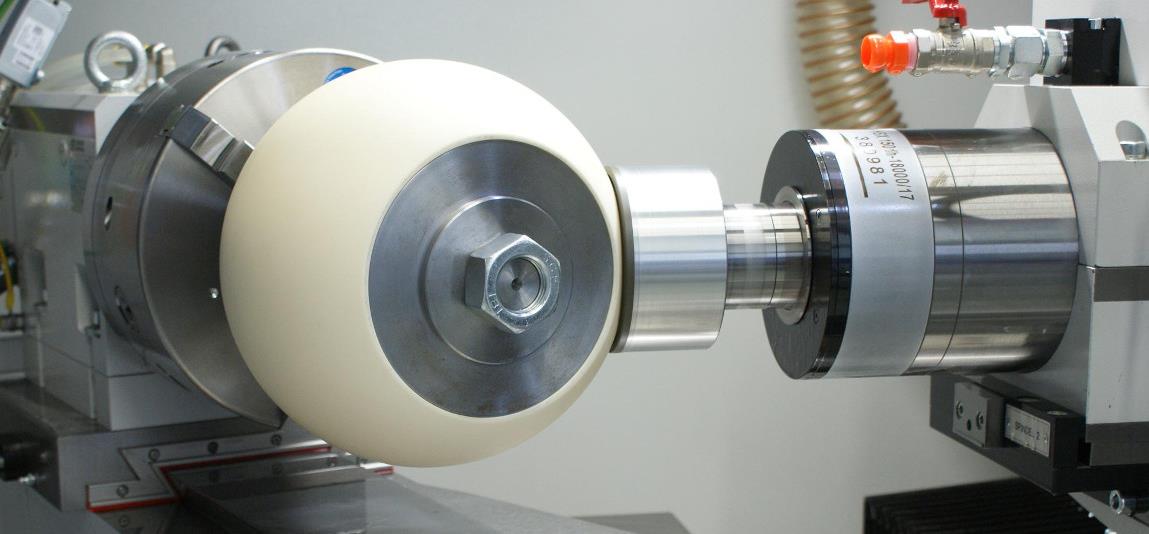
Ceramic machining technology refers to the technical process of machining soil into objects, is a complex and exquisite art, but also an important guarantee of the integrity and quality of ceramic products. Ceramic machining technology includes a series of operations such as crushing, forming, grinding, dressing and firing of ceramic materials.
First, the machining of ceramics overview
Because of its high hardness and brittleness, ceramics are difficult to carry out traditional processing methods, such as drilling, milling, grinding and so on. Therefore, the machining method of ceramics usually requires the help of special tools or processing equipment to complete, such as laser processing, chemical processing and so on.
Two, the main machining methods

Step 1 Grind
Grinding is a common machining method for ceramics. By grinding the grinding head on the ceramic surface to remove the material, thus achieving the effect of fine machining. The disadvantage is that the processing efficiency is low, and it is easy to produce thermal stress.
2. Turning
Turning is a machining method for mass production of ceramic parts. Commonly used in the manufacture of ceramic pipes, valves, bearings and so on. This method produces less heat loss during processing, but it is not effective in fine processing.
3. Milling
Milling is a machining method commonly used to manufacture ceramic plates and special-shaped parts. It can quickly remove ceramic materials and is suitable for work pieces of various shapes and sizes.
4. Laser processing
Laser machining is an efficient and flexible machining method for ceramics. It can achieve fine machining without causing thermal stress, and can achieve high-precision and high-efficiency ceramic machining.
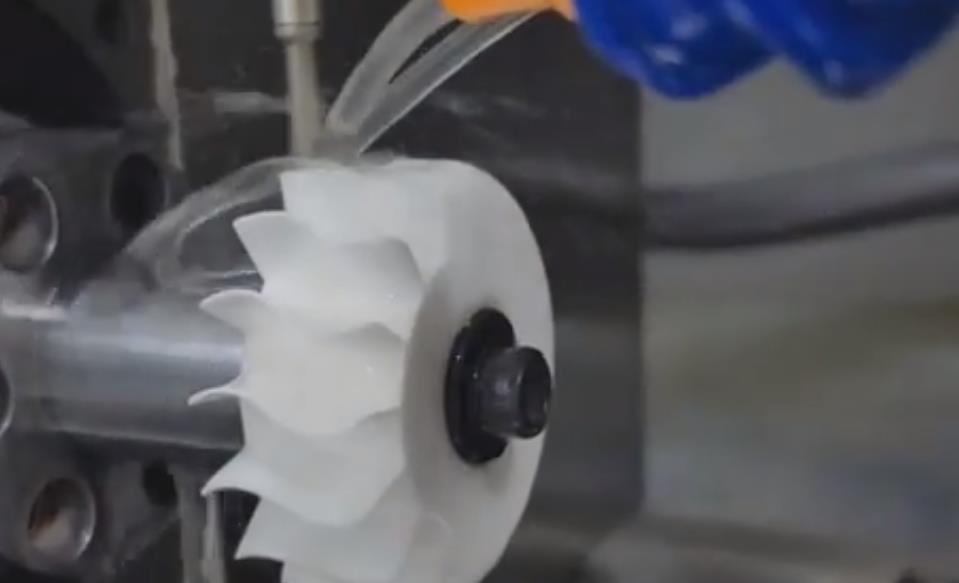
Third, the scope of application and advantages and disadvantages of machining methods
Step 1 Grind
Scope of application: Suitable for the size and surface finish requirements are not high, and the processing amount is not large ceramic parts.
Advantages: High machining precision, can precisely control the machining thickness.
Disadvantages: low processing efficiency, easy to produce thermal stress, not suitable for mass production.
2. Turning
Scope of application: Suitable for large scale, medium precision parts processing.
Advantages: High processing efficiency, workpiece size and surface accuracy stability.
Disadvantages: not suitable for high-precision machining, easy to produce surface cracks, not suitable for small size workpieces.
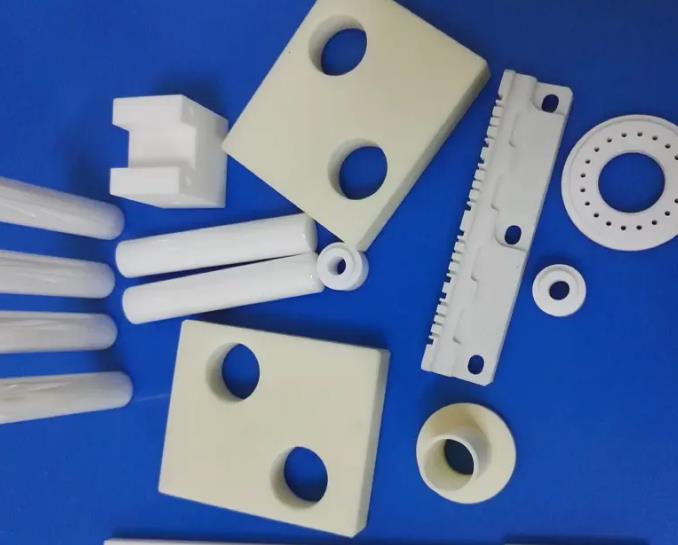

3. Milling
Scope of application: Suitable for mass production of medium precision ceramic parts.
Advantages: High processing efficiency, precise control of processing size and accuracy.
Disadvantages: not suitable for high-precision machining, easy to produce surface cracks.
4. Laser processing
Scope of application: Suitable for various shapes of ceramic parts, especially suitable for high-precision, small-batch production.
Advantages: High processing efficiency, high precision, no thermal stress and mechanical stress.
Disadvantages: High equipment cost, not suitable for large batch production.
Ceramic machining technology refers to the process steps of machining the original ceramic material into ceramic parts of the required shape and size by mechanical machining or other means. There are many kinds of ceramic machining technology, of which the most commonly used are machining, heat treatment, polishing, coating, surface softening and so on.
First, mechanical machining:
Machining refers to the process of using machine tools or other mechanical equipment to cut raw ceramic materials into ceramic parts of the required shape and size. Generally, machining processes include grinding, milling, cutting, drilling, sawing, etc.
Second, heat treatment:
Heat treatment technology refers to the heating and cooling of ceramic materials to achieve the required physical and mechanical properties of a series of technologies. Common heat treatment methods are heat treatment, heat treatment, welding, sintering and so on.
Third, polishing:
Polishing refers to the use of polishing machine or hand polishing, the ceramic surface machining into smooth, smooth, burr free, showing the gloss of the process steps. Polishing process commonly used are sandblasting polishing, hanging grinding wheel polishing, vibration polishing and polishing machine polishing.
Four, paint:
Coating refers to the process step of coating a layer of pigment on the ceramic surface to protect the surface and improve the color, strength and other properties. The types of coatings are lacquer, paint, glass fiber, metal powder and so on.
Five, surface softening:
Surface softening refers to the process step of machining the ceramic surface to make it soft to meet customer requirements. Common surface softening methods include drawing, grinding, oxidation and so on.
In summary, although ceramics are difficult to carry out traditional machining methods, there are many special machining methods that can be used for their manufacturing. Machining methods such as grinding, turning, milling and laser processing have their own characteristics and can be selected according to different ceramic materials and production requirements.